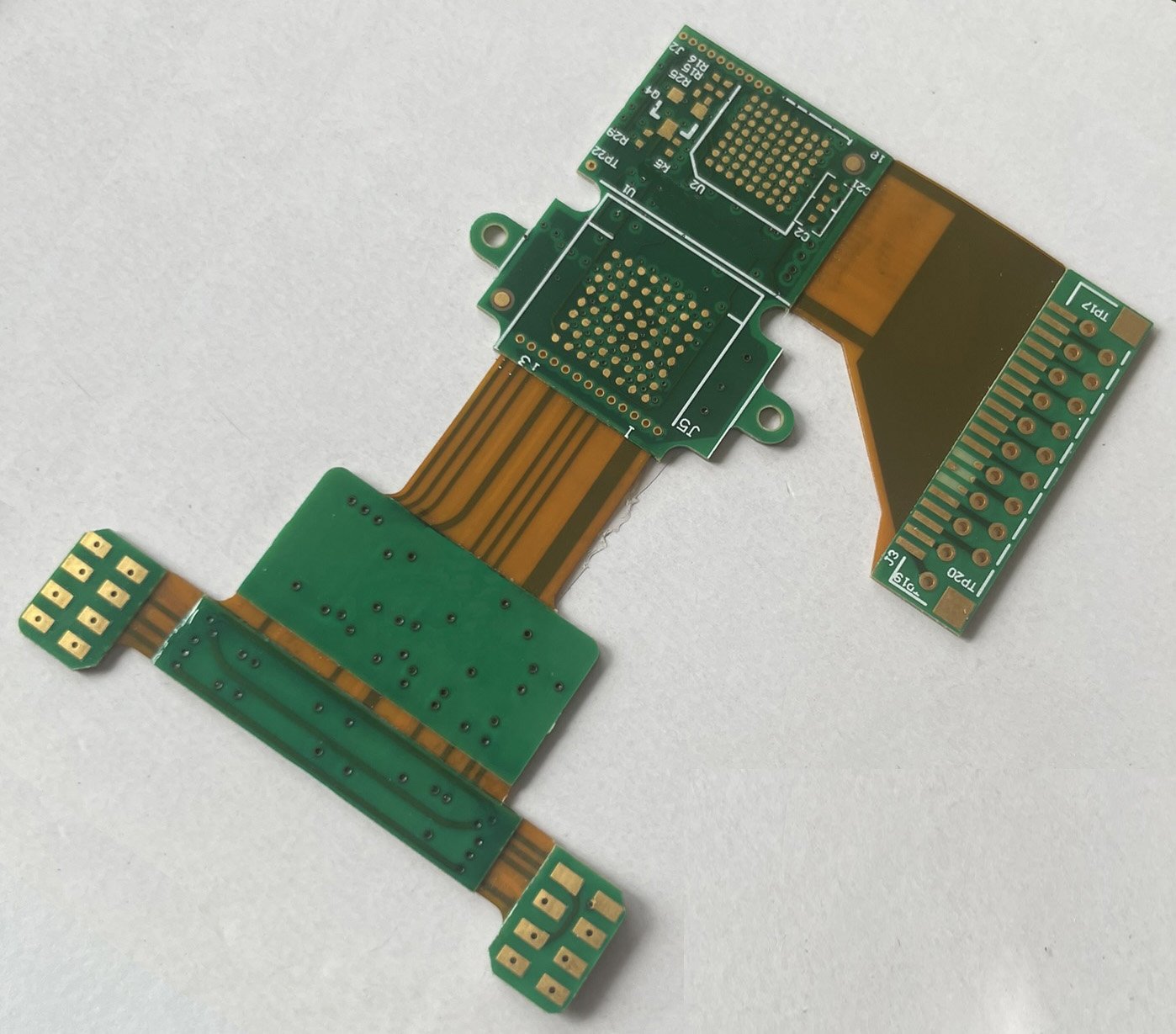
Rigid Flex Circuits
Rigid-flex circuits are advanced printed circuit boards (PCBs) that integrate both rigid and flexible substrates into a single interconnected structure. Ideal construction includes a balanced circuit construction with the flex circuit layer in the middle of the rigid flex. This hybrid design combines the mechanical stability of rigid boards with the adaptability of flexible circuits, offering unique advantages for complex electronic applications.
By combining the benefits of rigid PCBs and flexible circuits, rigid-flex technology offers a versatile solution for modern electronic designs, enabling more compact, reliable, and efficient devices.
Key Components
Integrated Structure: Rigid-flex circuits consist of multiple layers of flexible substrates attached to one or more rigid boards, either internally or externally, depending on the design requirements.
Three-Dimensional Configurations: The flexible sections allow the circuit to be bent or folded, enabling more compact and efficient use of space within electronic devices.
Advantages
Space and Weight Reduction: By eliminating the need for connectors and traditional round wire cables between separate rigid boards, rigid-flex designs can significantly reduce the overall size and weight of electronic assemblies.
Enhanced Reliability: The seamless integration of rigid and flexible sections minimizes the number of solder joints and connectors, reducing potential points of failure and improving the durability of the circuit.
Design Flexibility: Rigid-flex circuits provide greater freedom in designing electronic systems, allowing for innovative layouts that can conform to specific form factors and meet complex mechanical requirements.
Common Applications
Consumer Electronics: Utilized in smartphones, communication, and wearable devices where compact and reliable interconnections are essential.
Medical Devices: Employed in diagnostic and monitoring equipment that requires flexible yet robust circuitry to accommodate various form factors.
Automotive and Aerospace: Applied in control systems, sensors, and other critical components where durability and space optimization are crucial.